I began with watching an introduction to what electrcity is, how it works and what units are important to understand.
Some basics:
-
Electricity is the type of energy that can be built up in one place or flow from one place to another
-
Static electric charges is energy gathered in one place.
-
Current electricity is energy that flows from one place to another.
-
Current is the form of electricity which makes all our electronic gadgets work, when charges are able to constantly flow, dynamic, charges are always on the move.
-
DC current : the flow of electrons stays in the same direction and the voltage stays the same.
-
AC current : the flow of electrons changes & the voltage does not stay the same
-
Voltage is a force which makes electrons move through a wire.
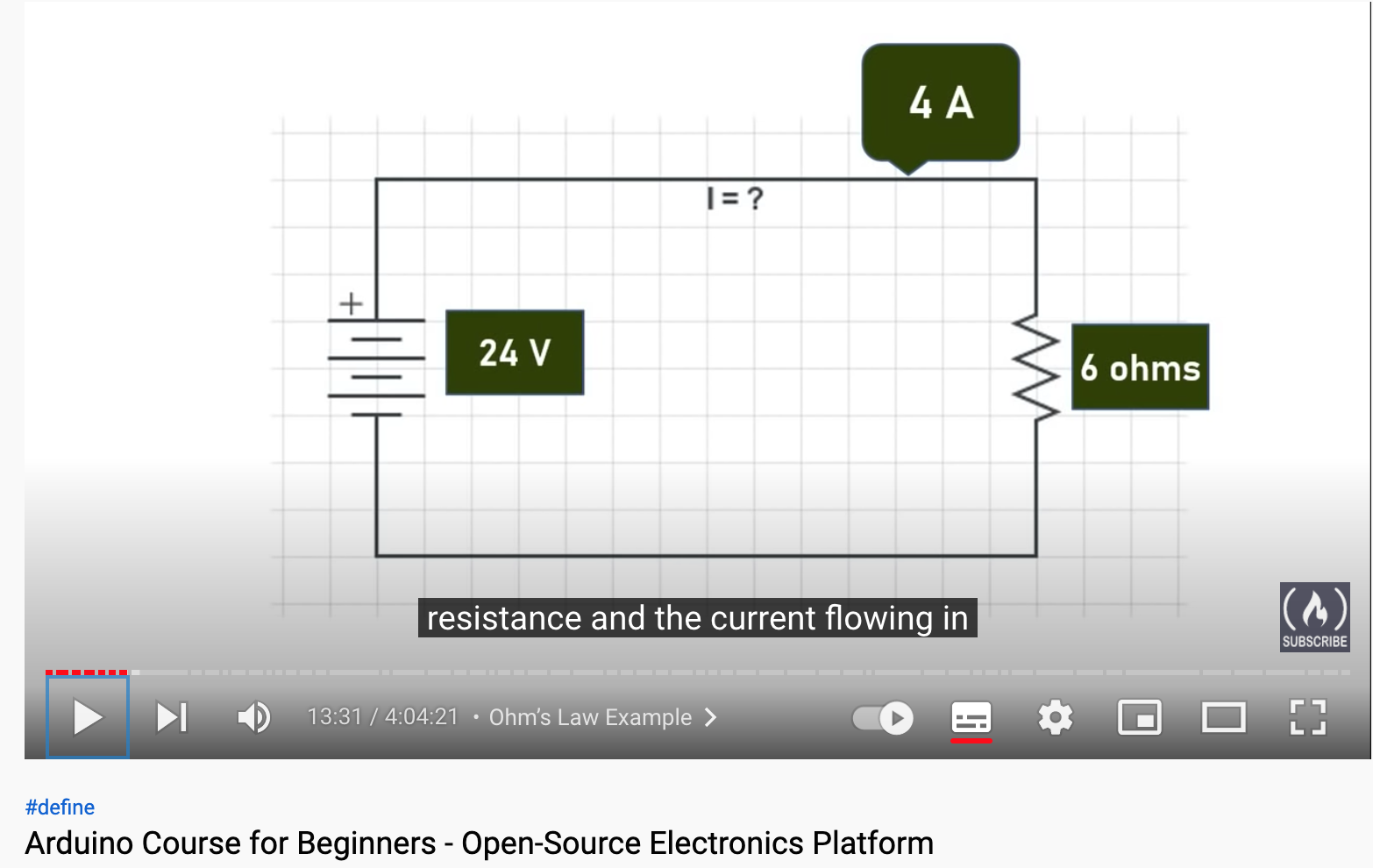 Electricity Introduction
Electricity Introduction
- Voltage V
- Current A or I
- Resistance ohms
V = I * R R = V/I I = V/R
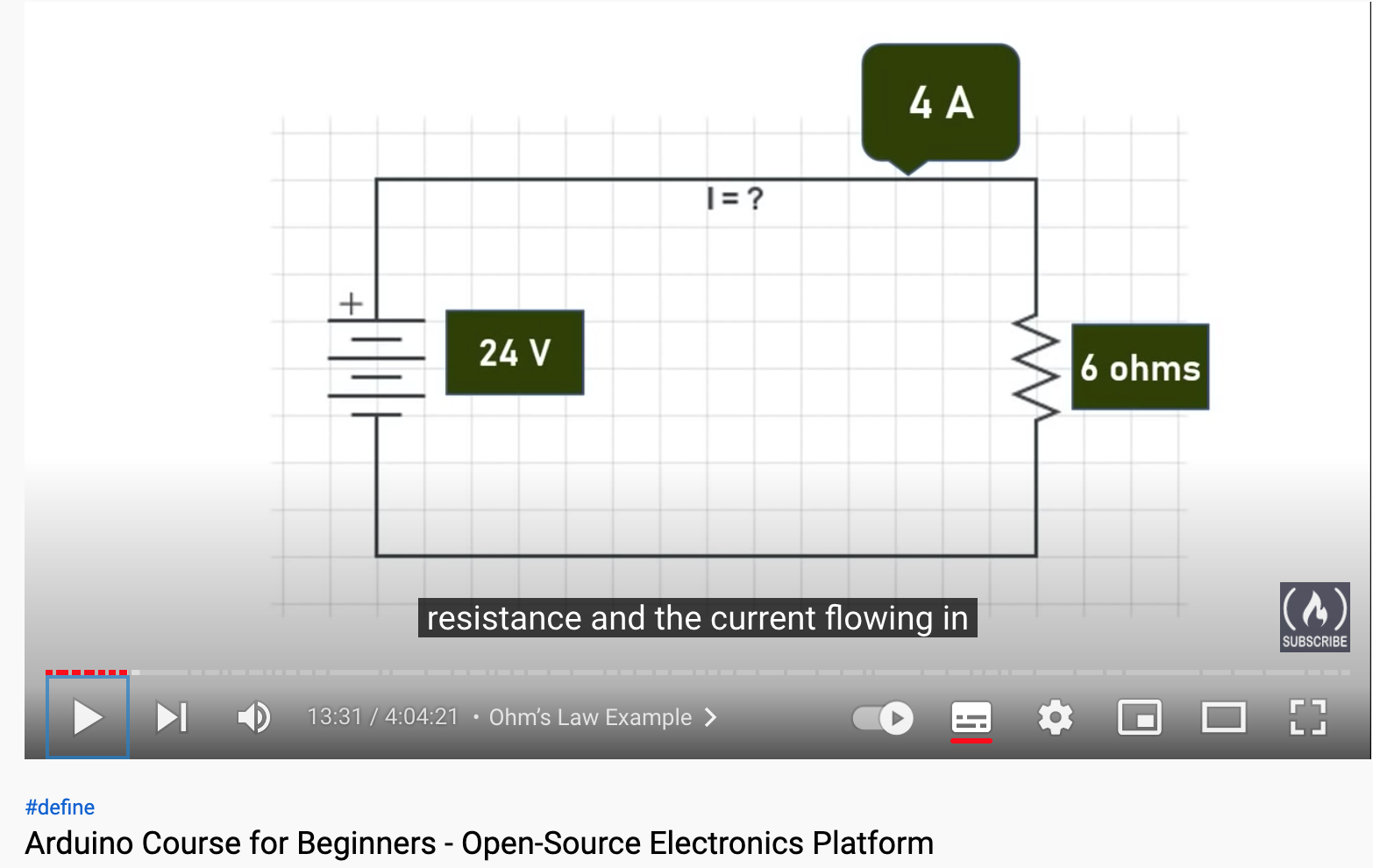 Resistance can be formed in series or in parallel
Resistance can be formed in series or in parallel
Microprocessor & Microcontroller
-
Microprocessor is known as the brain of any computer
IDE
Breadboard
Input Devices & Sensors
A sensor basically gives data to the arduino, it gives information to the controller by changing its voltage
Some examples
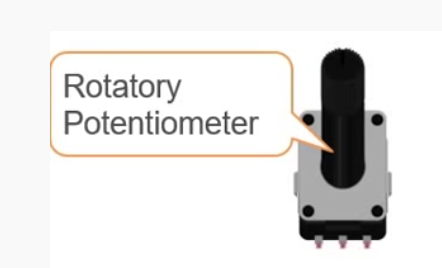 Rotatory Potentiometer: This device would change the resistance it offers if we rotate the knob clockwise or anti-clocwise
Rotatory Potentiometer: This device would change the resistance it offers if we rotate the knob clockwise or anti-clocwise
 Momentary Push Button Switch: When we press the switch it will close the circuit and when we release the switch it will open the circuit
Momentary Push Button Switch: When we press the switch it will close the circuit and when we release the switch it will open the circuit
Sound & Microphone Sensor Touch Sensor Rotary Encoder Ultrasonic Distance Sensor Infrared Sensor Temp & Humidity Sensor Light Dependant Resistor
Output Devices
Analog & Digital
Analog & Digital Signals
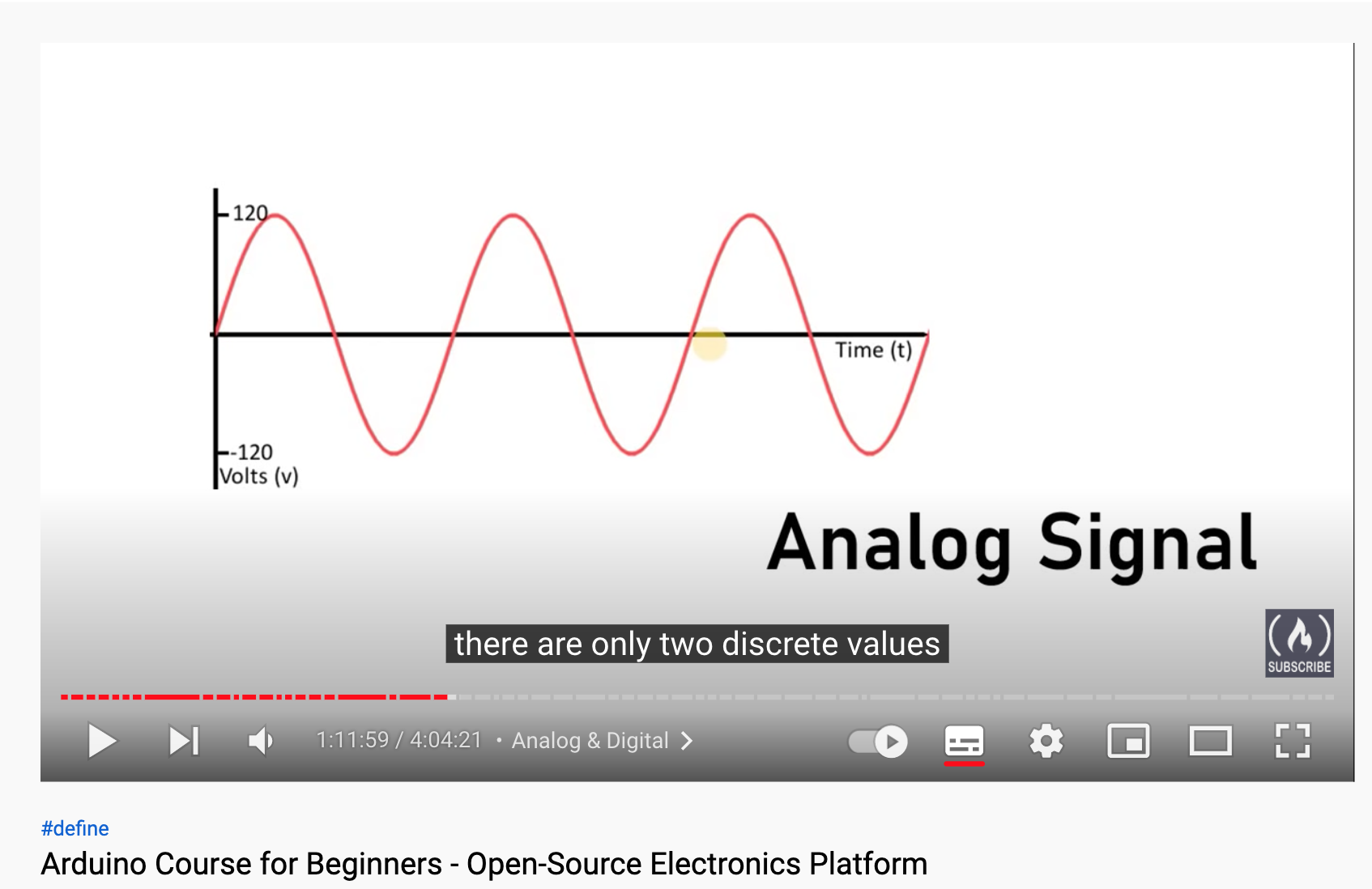 Analog Signal
Analog Signal
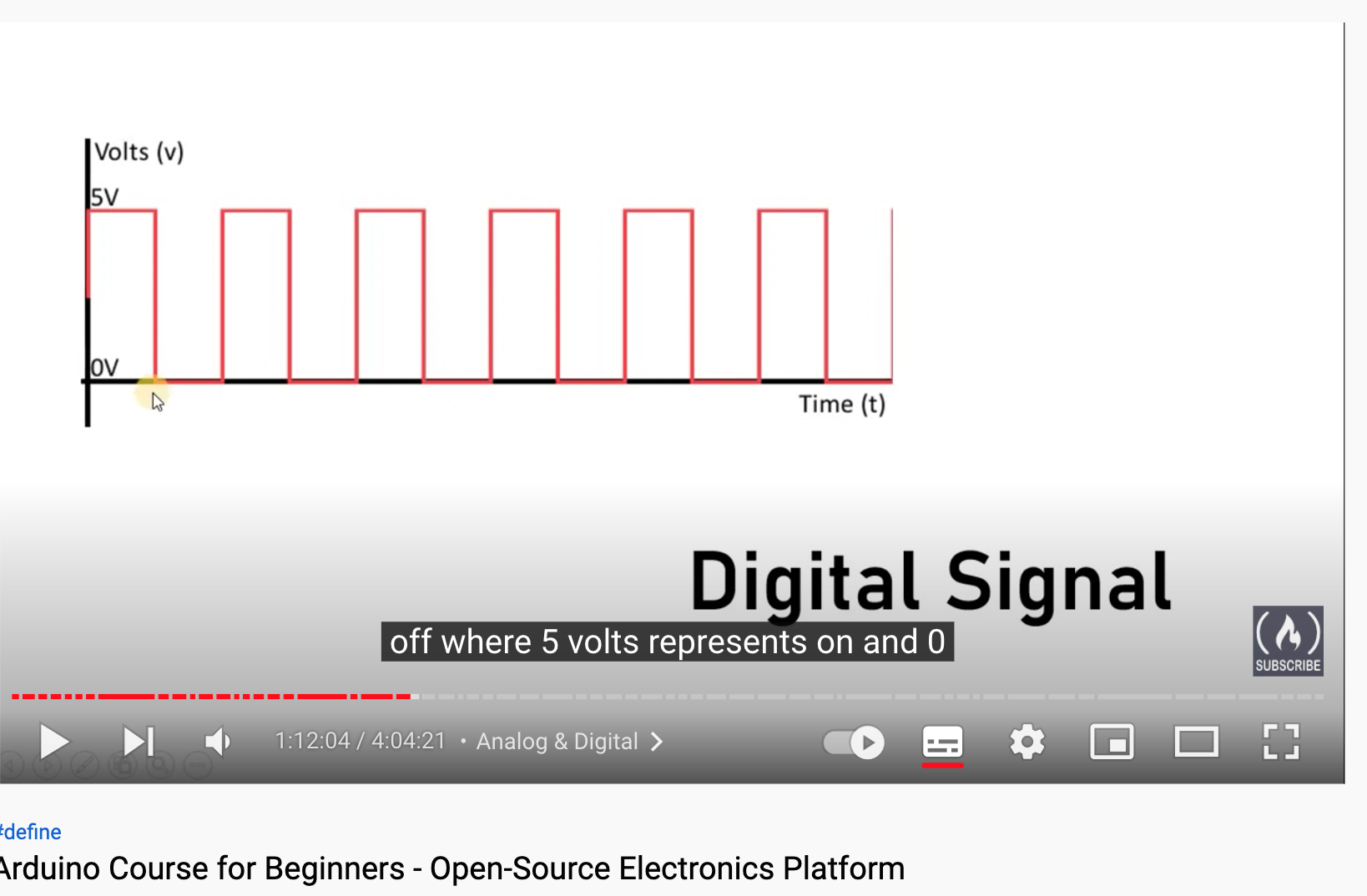 Digital Signal
Digital Signal
 Digital and Analog Sensors
Digital and Analog Sensors
Bits and Bytes
 Calculting bits
Calculting bits
*A bit can store 0 or 1 inside one memory box *8 bits form a byte
- We can only store value up to the upper limit of that space Need to research a bit on binary math ro understand it a bit better
- In order to calculate how many bits are needed, we multiply by 2
Arduino Programming
- Arduino programming uses a mixture of c and c++
- Arduino makers call it wiring
- Setup and Loop
- Built in functions
- what digitalWrite means is replace the built in function with a certain pin on the arduino board, n.13 for instance manipulating digital pins through inbuilt functions Low means 0 voltages which mean light off and high means 5 voltages which means ligh on *Variables, declared before setup
- Serial.begin(9600) enables communication between arduino and computer
- Serial.println will add an additional line after printing
- Increment (pre and post) for example myVariable++ instead of ++myVariable The difference is either use the increment then declare it or the opposite of declare then use
- Decrement is using - myVariable–
- int, float already familiar with them
- Note about bool : 1 or HIGH true holds the same value, any other number aside from 0 will be converted to 1, 0 or LOW or false holds the same value
- byte can store 8 bits of data, a byte is just like an int and the range is from 0 to 255, if byte is declared without a value it will initialize it as 0
- char is for characters, declaring one character, each character holds a certain value in numbers
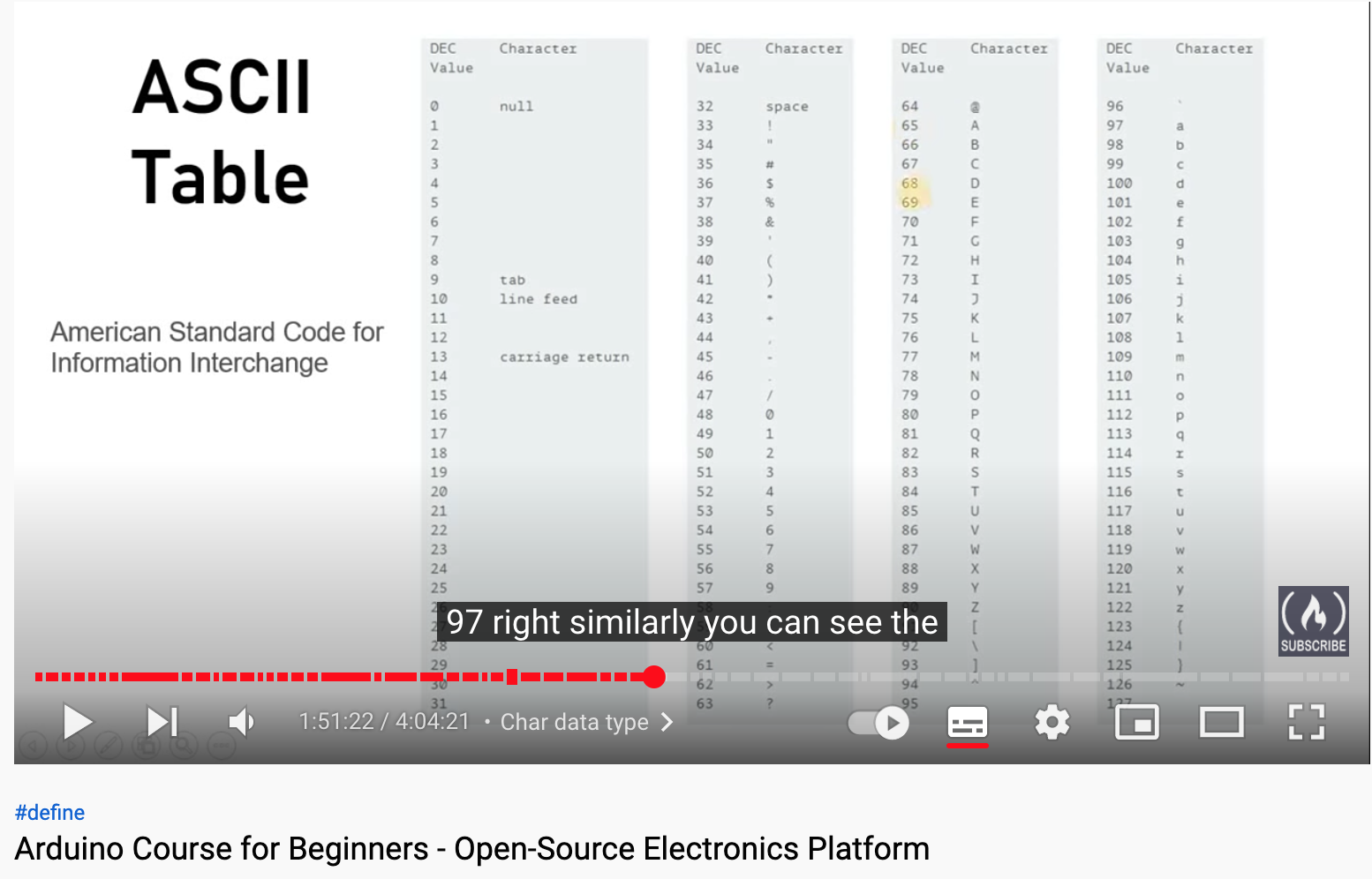 Character table
Character table
#### Variable Scope & Qualifiers
- Scope
-
Two types of variables : Global and local, already familiar with this, just note that if you declare a local varibale in void setup() you can also declae it again in void loop() with a different value
- Qualifiers define additional behavior to our variables, constant and static types… const keyword means its read only, can be used as any other variable of its type but its value cannot be changed
- you can use hash define instead of const, it doesn’t use any memory in arduino yet it has some downsides as the compiler will replace all the references to pi in the code and you will start facing problems *Static Qualifier will initialize a value locally only one time, for instance if declared inside void loop then it will only read it once static int fish = 0;
### Logical Operators
-
Also familiar with these ones, && !
Control Structues, same logic of if else statements while, do while…etc.. the break condition helps to break out of an endless loop the continue